
You may read the detailed principle of scaling or balancing on our previous article, Scaling of Base Shear Results from Static and Dynamic Analysis. Stay tuned for another article on how scaling is accomplished in ETABS to be posted soon. To properly distribute the forces, the base shear obtains or calculated from the dynamic analysis should be reduced to a certain percentage of the base shear results that is determined from the static force procedure.

Scale Factors or Balancing of Response Spectrum These overturning effects on every element shall be carried down into the foundation.įor further information, the summary of seismic provisions considering base shear and overturning effect as per UBC 97 and ASCE 7-10 has been discussed in previous articles, Seismic Analysis: UBC 97-Provisions and Seismic Analysis: ASCE 7 and IBC 12 Provisions respectively. The overturning effects caused by earthquake forces that act on levels above and below of every structure shall be resisted and design according to the code specified in UBC 97, Section 1630.5 or at Section 12.8.5 of ASCE 7-10. The base shear forces to use in the design will be calculated using the Auto Load Function of ETABS Program using the “Equivalent Lateral Force Procedure” and the “Dynamic Analysis Procedures” as set out in UBC 97 Response Spectrum Analyses or ASCE 7 whichever code is required in your design. The static base shear will be used to calculate scale factors for the model to be balanced with dynamic base shear as specified by the code. Static Force or the Equivalent Lateral Force Procedure of calculating base shear should perform under the UBC 97, clause 1630.2.1 and or as per Equation 12.8-1 of ASCE 7-10 codes. Base Shear Checkīase Shear, V is the total design lateral force or shear force at the base of the structure.
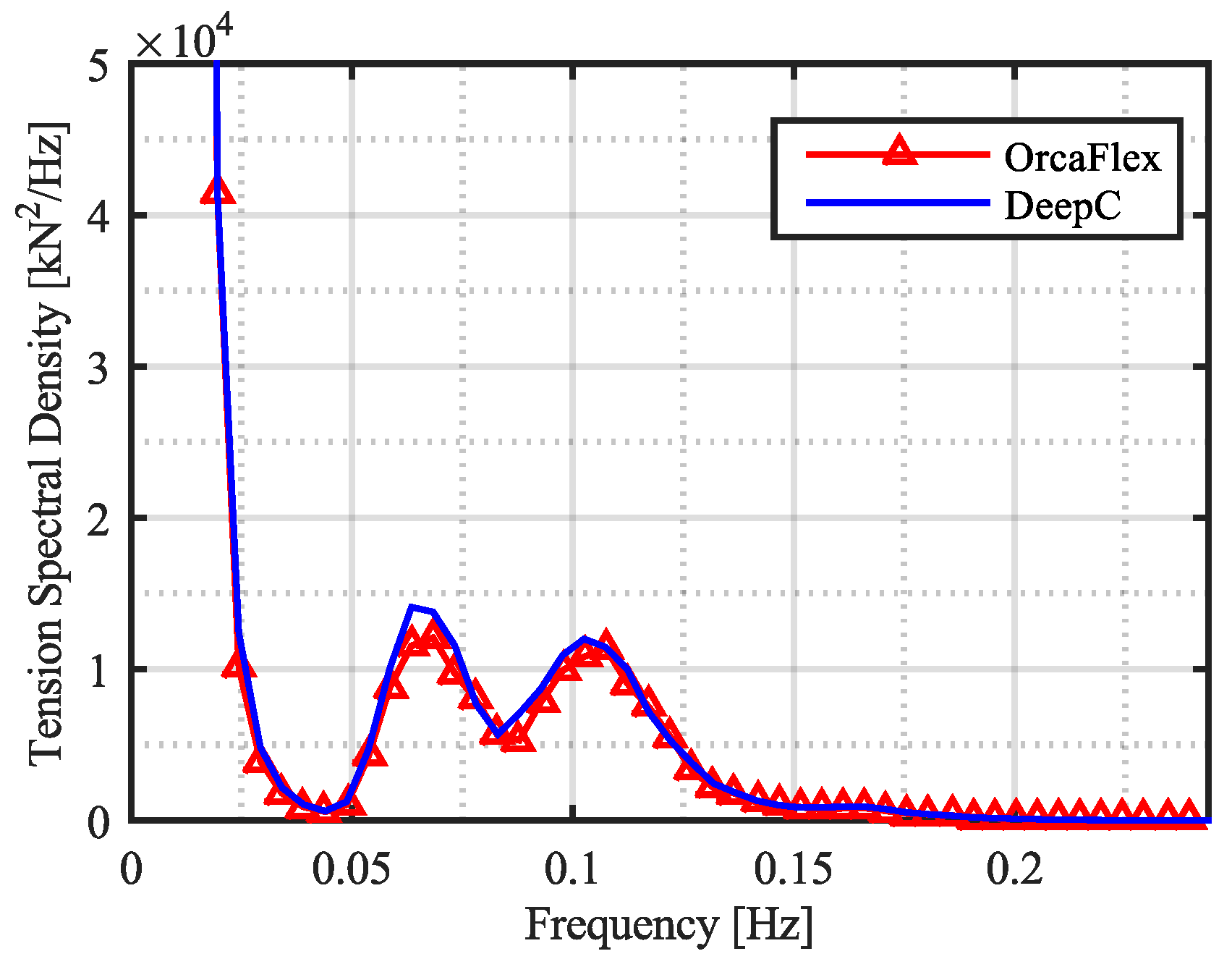
7 Dynamic Analysis Checks to Consider in Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis using ETABS 1. In this video you will learn how to utilized the pushover analysis and time history analysis a 3D RC building from A to Z. Apply Nonlinear Static Analysis and Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis using ETABS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
